Mastering Magnetic Declination with Evolution and Use of Declination Maps for Enhanced Navigation
Magnetic declination is a critical concept for accurate navigation as it accounts for the difference…….
Magnetic declination is a critical concept for accurate navigation as it accounts for the difference between a compass's magnetic north indication and the true geographic north pole. This variation, known as magnetic variation, arises from irregularities in the Earth's geomagnetic field and must be corrected to ensure precise bearings. Historically, compass accuracy has evolved significantly since ancient times, with advancements leading to modern digital declination maps based on satellite data like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and Beidou. These enhancements have rendered magnetic compasses and their electronic counterparts highly accurate tools for both traditional and contemporary navigation. In areas without reliable GPS signals, understanding and applying declination correction remains essential, as it allows for safe and efficient journey planning using a magnetic compass, which must be adjusted with the help of precise declination maps tailored to specific locations. The integration of declination correction in modern GPS systems and digital compasses has significantly improved navigation accuracy, making compasses, including their electronic variants, indispensable tools for outdoor enthusiasts, surveyors, and professionals who demand high precision in their navigational instruments.
Navigators and adventurers have long relied on the magnetic compass for orientation. This article delves into the intricacies of magnetic declination and its significance in ensuring accurate compass readings. We trace the historical trajectory of declination maps, from their rudimentary origins to the sophisticated methods employed today. Understanding how to interpret these maps is crucial for enhancing the reliability of traditional magnetic compasses. Furthermore, we explore the integration of declination data into modern GPS and digital compass systems, highlighting advancements that have revolutionized navigation tools. Join us as we align our bearings on the topic of declination maps and their role in precise compass navigation.
- Understanding Magnetic Declination and Its Impact on Compass Accuracy
- The Evolution of Declination Maps: Historical Perspectives to Modern Techniques
- How to Use Declination Maps to Enhance Your Magnetic Compass Navigation
- Advanced Applications: Integrating Declination Data in GPS Systems and Digital Compasses
Understanding Magnetic Declination and Its Impact on Compass Accuracy
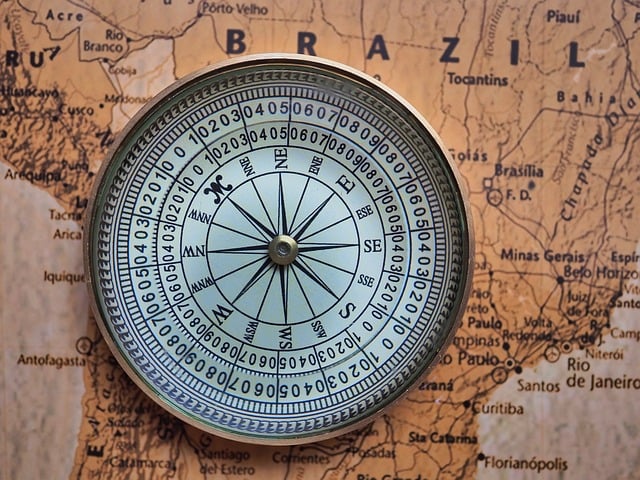

The concept of magnetic declination is pivotal in comprehending the true north from a compass’s indicated north when using a magnetic compass. Magnetic declination, also known as magnetic variation, arises due to the Earth’s geomagnetic field’s inconsistencies across its surface. It’s a measure of the difference between the magnetic north pole and the geometric or true north pole. This discrepancy can lead to significant errors if not accounted for, particularly in navigation where precision is paramount. For instance, in certain regions, a compass might point towards the magnetic north, while the true north might be significantly different. Understanding and correcting for declination is essential for accurate navigation, as it allows navigators to adjust their magnetic bearings to true bearings, ensuring they are heading in the intended direction.
Navigators relying on magnetic compasses must consult declination maps or use electronic instruments that compensate for this variation. These maps indicate the amount of west or east one must correct a magnetic reading to get the true bearing. The impact of magnetic declination on compass accuracy is substantial, especially over long distances where even small deviations can result in significant errors. As such, accurately interpreting and applying declination data is a critical skill for anyone involved in traditional navigation techniques. With the advent of technology, digital compasses can automatically adjust for magnetic declination, providing users with true headings. However, understanding the principles behind this correction remains indispensable, as it ensures that whether using a traditional magnetic compass or a modern electronic one, the user can navigate with confidence and accuracy.
The Evolution of Declination Maps: Historical Perspectives to Modern Techniques

The concept of compass accuracy has been a subject of interest and innovation for centuries, with the earliest forms of compasses dating back to the ancient Chinese in the 1st century AD. Over time, as mariners ventured further from familiar shores, the need for precise navigation tools became paramount. Declination maps, which illustrate the difference between magnetic north and true geographic north, have evolved significantly from their historical origins to modern times. Initially, these maps were simple charts indicating the variation, or the angle between the magnetic north and the geographic north. With the advent of the 19th century, improvements in surveying techniques and the understanding of Earth’s magnetism led to more precise declination maps. The magnetic compass, an indispensable tool for seafarers, required accurate declination maps to maintain correct orientation, which were often hand-drawn from local observations and published for wider use.
In the modern era, advancements in technology have revolutionized the creation of declination maps. Today’s magnetic compass users benefit from precise digital models that incorporate global data sets. These sophisticated maps are constructed using satellite-based measurements from systems like the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), which include the American GPS, the Russian GLONASS, the European Galileo, and the Chinese Beidou networks. This technology allows for real-time adjustments to declination maps as Earth’s magnetic field shifts over time. Consequently, the accuracy of compass readings has been greatly improved, ensuring that modern navigators can rely on their instruments with a high degree of confidence, whether they are charting a course across open oceans or hiking through uncharted territories.
How to Use Declination Maps to Enhance Your Magnetic Compass Navigation

When venturing into territories where GPS signals are unreliable or unavailable, a magnetic compass becomes an indispensable tool for navigation. To ensure accurate bearings with your compass, it’s crucial to account for the Earth’s magnetic field and its variation in different regions. This is where declination maps come into play; they provide precise data on the angle between true north and magnetic north at a specific location.
To begin, locate a reliable declination map for your intended area of exploration. These maps can often be found online or within topographic maps and atlases. Once you have the declination map, align your compass by adjusting its magnetic needle or using an adjustable compass model where you can set the declination. For a fixed magnetic compass, subtract or add the local declination value to your magnetic reading to determine the true direction of travel. This process effectively corrects for the compass’s inherent error, allowing for more precise navigation. By consistently referencing and applying declination maps, even in environments where satellite-based systems fail, you can confidently rely on your magnetic compass to guide your journey safely and efficiently.
Advanced Applications: Integrating Declination Data in GPS Systems and Digital Compasses

In modern navigation, integrating declination data within GPS systems and digital compasses has become a cornerstone for ensuring precise directional readings. Traditional magnetic compasses rely on Earth’s magnetic field to determine cardinal directions; however, due to geographic variation in this field, known as declination, their readings can be off by several degrees. This discrepancy can lead to significant navigation errors, especially over long distances. Advanced applications have addressed this issue by incorporating up-to-date declination maps into GPS and digital compass technologies. These systems use the precise location data provided by GPS satellites in conjunction with pre-calibrated declination information to provide users with corrected headings. This fusion of GPS accuracy with magnetic compass technology not only enhances the reliability of directional navigation but also simplifies the user experience, as it eliminates the need for manual declination adjustments. The result is a seamless and highly accurate tool for outdoor enthusiasts, surveyors, and anyone who relies on accurate navigation systems, ensuring that their intended course is true regardless of local magnetic anomalies.
The integration of declination data in GPS-enabled compasses is a testament to the ongoing innovation in the field of navigation technology. As these systems continue to evolve, they are becoming increasingly sophisticated, incorporating additional sensors and algorithms to further refine their accuracy. For instance, some advanced models can adjust for not only magnetic declination but also for the effects of local topography and even human magnetic interference. This level of precision is invaluable for applications that demand high-accuracy navigation, such as search and rescue operations, large-scale land surveying, or scientific field studies. The evolution of digital compasses with integrated declination data underscores the importance of adapting to the ever-changing landscape of technological advancement, ensuring that navigational tools remain robust and reliable for all users.









